Papillomas on the neck do not create noticeable discomfort, but they spoil the appearance. These neoplasms grow when the human papillomavirus (HPV) enters the body. The only exception is the growths, which are often damaged. To get rid of papillomas on the neck, specialized (most often surgical) intervention will be required.
Causes
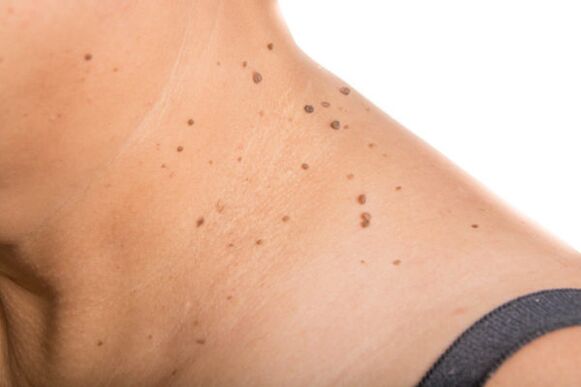
Papillomas are benign neoplasms that result from HPV infection. Doctors isolate more than a hundred viruses that can cause the appearance of such growths on the body. Hanging warts of small sizes often appear on the neck, they reach 2-3 cm in diameter.
Human papillomavirus infection occurs through direct contact with an HPV carrier. It is also possible to transmit the pathogen through personal hygiene items or clothing. The virus can enter the child's body in utero or during childbirth.
The likelihood of papillomas directly depends on the state of immunity. With a weakened body defense, the first growths appear several days after infection.

The reasons for the appearance of neoplasms on the neck include:
- frequent damage to the skin epithelium;
- allergic reactions;
- severe stress;
- respiratory diseases, helminthic invasions;
- long-term use of a number of medications;
- overweight;
- bad habits;
- non-observance of hygiene rules.
In women, hormonal imbalance during pregnancy, during menopause, or due to taking contraceptives is considered one of the common causes of the formation of growths.
If small growths appear on the neck, then often specialized treatment is not required. In the absence of exposure to provoking factors, such warts disappear without outside intervention in three years.
Types and symptoms
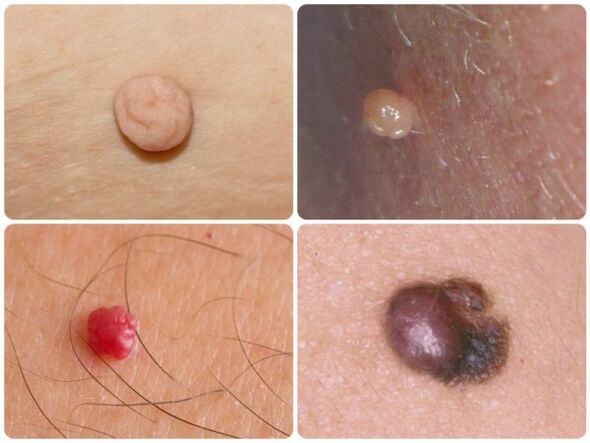
Of all types of papillomas on the neck, growths of the following types arise:
- Filiform- look like small bumps with a yellowish surface. In the future, a leg appears, through which the growth is attached to the skin. Filiform papillomas are flesh-colored or light brown in color.
- Flat- formations of this type protrude slightly above the cervical surface. The color of flat growths does not differ from the shade of neighboring tissues. Over time, they merge with each other, thereby increasing the affected area, and sometimes itch.
- Keratopapillomas- occur mainly in people over 30 years old, are round or longitudinal.
- Seborrheic- are distinguished by the presence of a flaky surface. These growths are often painful.
- Simple (vulgar)- this type of papillomas is localized on the upper limbs, but they also sometimes grow on the neck or face. The growths look like rounded warts, protruding significantly above the skin.
Most papillomas are single. But in the case of injury to the affected area or against the background of a sharply weakened immunity, the virus spreads to new areas, which leads to the appearance of multiple neoplasms.

The growth of papillomas is not accompanied by severe symptoms. In rare cases, the activity of the virus causes:
- itching;
- burning;
- pain.
When the problem area is injured, the affected areas begin to bleed.
Possible consequences
Complications caused by the activity of the papillomavirus are often caused by the actions of the carrier of the infection. Frequent injury to growths causes:
- Development of papillomatosis. This pathology is characterized by multiple growths that form on a small area of the body. In extreme cases, the entire cervical region is affected. This is explained by the fact that each wart contains the smallest particles of the virus, which, when the neoplasm is injured, spread to healthy areas.
- Degeneration into a malignant tumor. Malignancy is also more often due to the trauma of neoplasms. Damage leads to the development of an inflammatory process in problem areas.
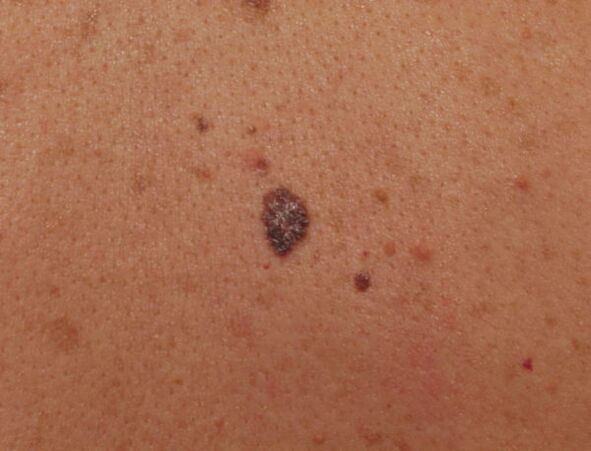
Papillomas on the neck are more often exposed to external influences, as a result of which open wounds form on the skin. Because of this, the affected area is often infected with pathogenic bacteria, which leads to inflammation and suppuration of the epidermis.
Therefore, if the wart comes off and bleeding begins in the problem area, it is necessary to treat the damaged skin with an antiseptic composition and close it with a bactericidal plaster. In addition, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist within two to three days to rule out the likelihood of complications.
Diagnostics
The papillomavirus causes characteristic growths. However, in some cases, it is not possible to differentiate warts from other similar neoplasms.
To exclude other diseases manifested in the form of skin rashes, the following diagnostic measures are carried out:
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction). Allows not only to diagnose the presence of a virus in the body, but also to assess the likelihood of tumor degeneration.
- Histological analysis. It is prescribed for suspicion of a malignant tumor.

The Digine test is considered more effective. This method is highly sensitive and provides information on the presence of papillomavirus, the strain of infection and the degree of oncogenicity.
Therapeutic techniques
To remove papillomas on the neck, you need to see a dermatologist. It is not recommended to independently engage in the removal of neoplasms from the skin. This is especially true in cases of multiple tissue damage, which indicates an immunodeficiency state.
In the treatment of papillomavirus, hardware techniques and medications are used. The latter cope well with single growths of a small size.
Drug therapy
Medication therapy is carried out mainly with the use of topical preparations.
To quickly remove warts from the neck, you can use special pharmacy products.
The use of drugs does not always help get rid of papillomas. Moreover, this method of treatment does not exclude the possibility of the appearance of neoplasms in the same place.
Hardware techniques
To remove papillomas from the neck, the following hardware removal techniques are used:
- Laser coagulation- allows you to remove neoplasms from the skin with minimal risk of infection or bleeding.
- Cryodestruction- the procedure provides for the treatment of problem areas with liquid nitrogen, which destroys tumor cells.
- Electrocoagulation- tumors are removed by exposure to high frequency current. This method is more painful than previously described.
- Radio wave removal- the method allows not only to remove the tumor, but also to take tissue for subsequent histological examination.
In rare cases, removal of the tumor from the neck is performed with the help of surgery.
ethnoscience
Home treatment can be done with folk remedies. They help to remove not only the smallest tumors, but are also effective in the fight against large growths.

To cope with papillomas on the neck will help:
- olive or castor oil. With this tool, it is necessary to lubricate problem areas several times a day;
- apple cider vinegar or ammonia. Any of these funds must first be applied to a cotton swab and applied to the build-up for a few minutes. The procedure should be carried out no more than once a day;
- aloe juice. They need to soak a cotton swab, which is applied to problem areas and kept for 4-5 hours;
- tea tree oil. It is enough to apply two drops of the product daily to the skin neoplasm;
- tincture of celandine. To prepare it, you will need to mix the plant juice with water in equal proportions. The product is infused for two weeks in a dark place. The resulting medicine should be drunk every day, 15 drops.
Regardless of the chosen method of combating papillomavirus, treatment must be supplemented with measures aimed at strengthening immunity. For this, it is recommended to take vitamin complexes and immunomodulators. From traditional medicine, decoctions from herbal preparations of lemon balm, plantain, dandelion root and other plants help to strengthen the immune system.
Prophylaxis
It is quite difficult to prevent human papillomavirus infection. But if you follow the rules of prevention, you can avoid the appearance of neoplasms on the body. This requires:
- wash hands and body daily;
- Healthy food;
- treat diseases in a timely manner;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- lead an active and healthy lifestyle.
If warts appear on the neck, it is recommended to be examined by a doctor in order to exclude malignant neoplasms. It is imperative to consult a dermatologist if the wart has changed color or multiple growths appear on the skin.























